Leucoencefalopatía multifocal progresiva, una entidad rara con un desenlace fatal. Presentación de caso
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.300Palabras clave:
Leucoencefalopatía progresiva multifocal, Virus JC, Síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida, NeuroimagenResumen
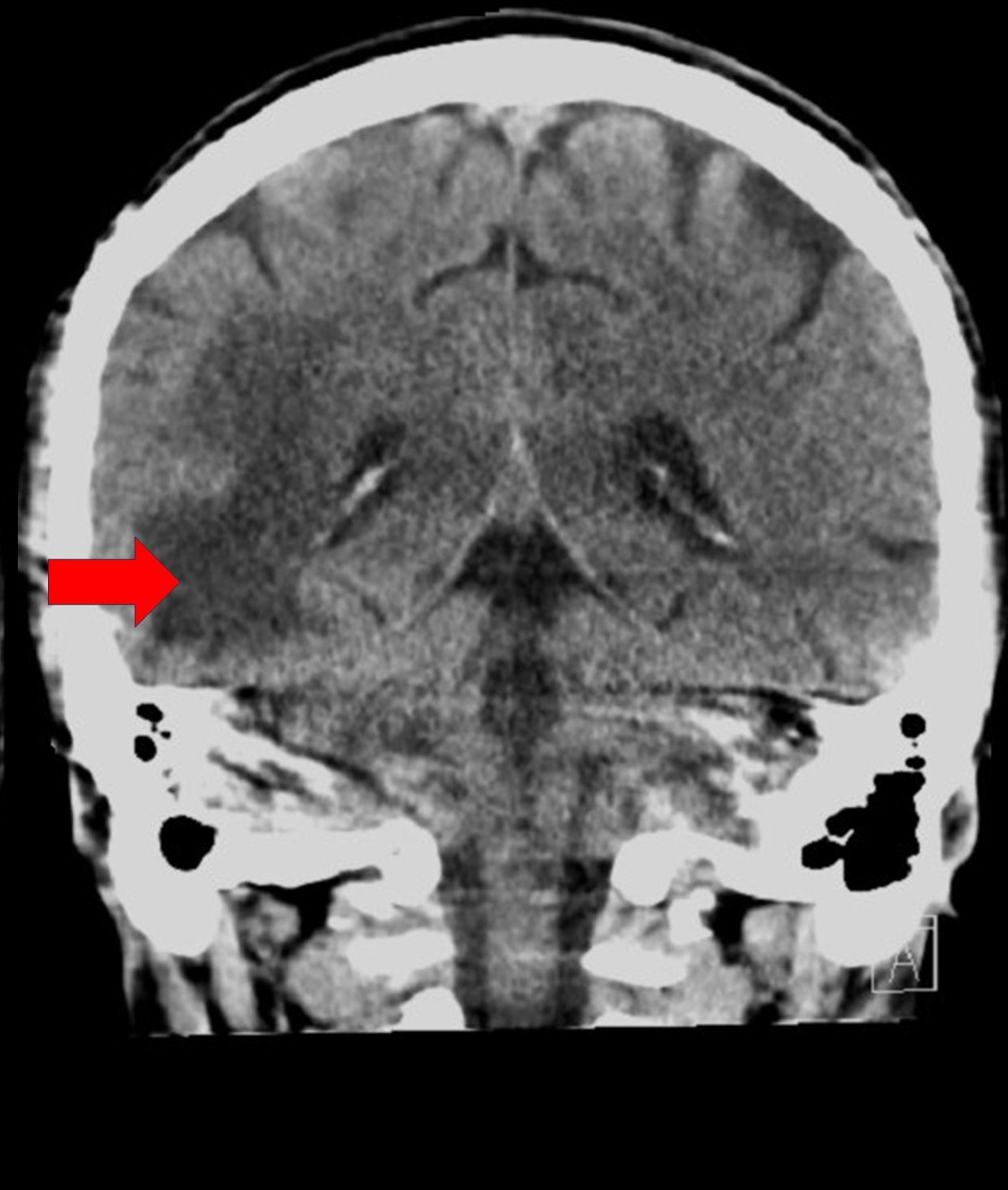
La leucoencefalopatía multifocal progresiva (LMP) es una infección oportunista causada por la reactivación del virus neurotrófico John Cunningham, el cual desarrolla un proceso infeccioso en casos de inmunosupresión grave. La resonancia magnética es el método de imagen preferido para el diagnóstico. Las características por imagen incluyen la identificación de áreas asimétricas y generalizadas en la sustancia blanca, con alta intensidad en señal en secuencias potenciadas en T2, escaso efecto de masa, restricción a la difusión y escaso realce tras la administración del medio de contraste. Se presenta el caso de un paciente de 31 años de edad, con un curso clínico de deterioro neurocognitivo, con hallazgos en la resonancia magnética compatibles con LPM. Se describirán las principales características y puntos clave para el diagnóstico imagenológico.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Moens U, Krumbholz A, Ehlers B, Zell R, Johne R, Calvignac-Spencer S, et al. Biology, evolution, and medical importance of polyomaviruses: An update. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;54:18-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2017.06.011
Monaco MC, Atwood WJ, Gravell M, Tornatore CS, Major EO. JC virus infection ofhematopoietic progenitor cells, primary B lymphocytes, and tonsillar stromal cells: implications for viral latency. J Virol. 1996;70(10):7004-12. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.70.10.7004-7012.1996
Cortese I, Reich DS, Nath A. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and the spectrum of JC virus-related disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(1):37-51. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-020-00427-y
Berger JR, Aksamit AJ, Clifford DB, Davis L, Koralnik U, Sejvar J, et al. PML diagnostic criteria: consensus statement from the AAN Neuroinfectious Disease Section. Neurology. 2013;80(15):1430-8. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828c2fa1
Garrels K, Kucharczyk W, Wortzman G, Shandling M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical and MR response to treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996;17(3):597-600. PMID: 8881262; PMCID: PMC8337997
Bezuidenhout AF, Andronikou S, Ackermann C, Du Plessis AM, Basson D, Bhadelia R. A. “Barbell Sign”: A diagnostic imaging finding in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Comp Assist Tomog. 2018;42(4):527-30 https://doi.org/10.1097/RCT.0000000000000719
Adra N, Goodheart AE, Rapalino O, Caruso P, Mukerji SS, González R, et al. MRI shrimp sign in cerebellar progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: description and validation of a novel observation. Am J Neuroradiol. 2021;42(6)1073-9. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A7145
Yousry TA, Pelletier D, Cadavid D, Gass A, Richert N, Raude E, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging pattern in natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:779-87. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23676
Wattjes MP, Vennegoor A, Steenwijk MD, de Vos M, Killestein J, van Ooste B, et al. MRI pattern in asymptomatic natalizumab-associated PML. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 2015;86:793-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2014-308630
Bergui M, Bradac GB, Oguz KK, Boghi A, Geda C, Gatti G, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: diffusion-weighted imaging and pathological correlations. Neuroradiology. 2004;46(1):22-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1115-9
Cosottini M, Tavarelli C, Del Bono L, Doria G, Giannelli M, De Cori S, et al. Diffusionweighted imaging in patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Eur Radiol. 2008;18(5):1024-30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0845-1
Küker K, Mader I, Nägele T, Uhl M, Adolph C, Klose U, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: value of diffusion-weighted and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosis and treatment control. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(8):819-26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01362.x
Mader I, Herrlinger U, Klose U, Schmidt F, Küker W. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: analysis of lesion development with diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroradiology. 2003;45(10):717-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-0966-4
Iranzo A, Moreno A, Pujol J, Martí-Fábregas J, Domingo P, Molet J, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy pattern of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in AIDS. J Neurol, Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;66(4):520-3. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.66.4.520
Williamson EML, Berger JR. Diagnosis and treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with multiple sclerosis therapies. Neurotherapeutics. 2017;14(4):961-73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-017-0570-7
Cinque P, Koralnik IJ, Gerevini S, Miro JM, Price RW. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in HIV-1 infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9(10):625-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70226-9
Fournier A, Martin-Blondel G, Lechapt-Zalcman E, Dina J, Kazemi A, Verdon R, et al. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome unmasking or worsening aids-related progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a literature review. Front Immunol. 2017;8:577. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00577
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 Revista colombiana de radiología

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.