Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome, a rare entity in pediatrics. About a case
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.197Keywords:
Porencephaly, Magnetic resonance imaging, SARS-CoV-2Abstract
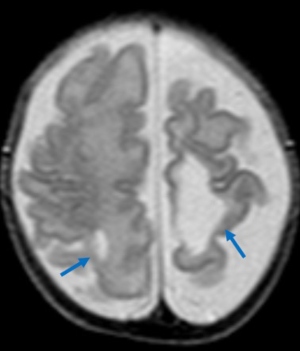
Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome is a clinical-radiological entity characterized by loss of the volume of a cerebral hemisphere with ipsilateral hypertrophy of the skull, elevation of the sphenoid wing and the petrosal edge of the temporal bone, as well as hyperpneumatization of the frontal sinus and mastoid cells associated with contralateral hemiplegia, facial asymmetry, seizures and intellectual disability. Initially described in 1933 by Dyke, Davidoff, and Masson. It mainly affects the pediatric age, and is attributed to an intrauterine or perinatal insult that affects the perfusion of a cerebral hemisphere. It may be of congenital or acquired origin (infectious, ischemic, hemorrhagic or tumor); its frequency is unknown since the diagnosis is usually established at ages outside the pediatric age range. The correlation between the clinical and neuroimaging characteristics are fundamental for its correct identification. Management is mainly symptomatic, including anticonvulsant medication for epilepsy and infant rehabilitation. We describe an unusual case with clinical and imaging features consistent with an early diagnosis of Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome with maternal history of
in utero damage risk.
Downloads
References
Dilber B, Sahin S, Eyüboğlu İ, Kamaşak T, Acar Arslan E, Durgut BD, et al. Two different manifestations of neonatal vascular injury: Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome and crossed cerebellar atrophy. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29(3):104600.
Sharma B, Nagpal K, Handa R, Bhana I. Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome: a clinicoradiological amalgam. Case Rep. 2014;2014:bcr2014204679.
Gökçe E, Beyhan M, Sade R. Radiological imaging findings of Dyke–Davidoff–Masson syndrome. Acta Neurol Belg. 2017;117(4):885-93.
Atalar MH, Icagasioglu D, Tas F. Cerebral hemiatrophy (Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome) in childhood: Clinicoradiological analysis of 19 cases. Pediatr Int. 2007;49(1):70-5.
Li Y, Zhang T, Li B, Li J, Wang L, Jiang Z. A potential cause of adolescent onset Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(51):e18075.
Dyke CG, Davidoff LM, Masson CB. Cerebral hemiatrophy with homolateral hypertrophy of the skull and sinuses. Surg Gynecol Obstetrics. 1933;57:588-600.
Aggarwal A, Aggarwal AK, Kapoor A, Kapoor R, Bansal A. Hemiatrophy of brain: antenatal ultrasonography and MRI/postnatal MRI diagnosis with the introduction of “shifted falx sign”. J Med Ultrason. 2017;44(1):147-51.
Piro E, Piccione M, Marrone G, Giuffrè M, Corsello G. Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome: case report of fetal unilateral ventriculomegaly and hypoplastic left middle cerebral artery. Ital J Pediatr. 2013;39(1):32.
Shen WC, Chen CC, Lee SK, Ho YJ, Lee KR. Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral hemiatrophy. J Formos Med Assoc Taiwan Yi Zhi. 1993;92(11):995-1000.
Gupta R, Joshi S, Mittal A, Luthra I, Mittal P, Verma V. Magnetic resonance imaging depiction of acquired Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome with crossed cerebrocerebellar diaschisis: Report of two cases. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2015;10(3):294.
Chetty S. A case report on a Dyke Davidoff Masson syndrome with right hemisphere involvement. South African Radiographer. 2016;54(1):12-14.
Duncana M, Vázquez-Flores S, Chávez-Lluévanos E, Cantú-Salinas A, León-Flores L, Villarreal-Velázquez H. (2014). Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome: A case study. Medicina Universitaria, 2014;16(73):71-3.
Dipan C, Patel BP. Neuron–glia interactions in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Nature reviews. Neuroscience. 2019;283-297.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista Colombiana de Radiología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.