Case study: Inflammatory processes in the neck, an imminent risk.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.271Keywords:
Soft tissue infections, Cellulitis, Ludwig’s AnginaAbstract
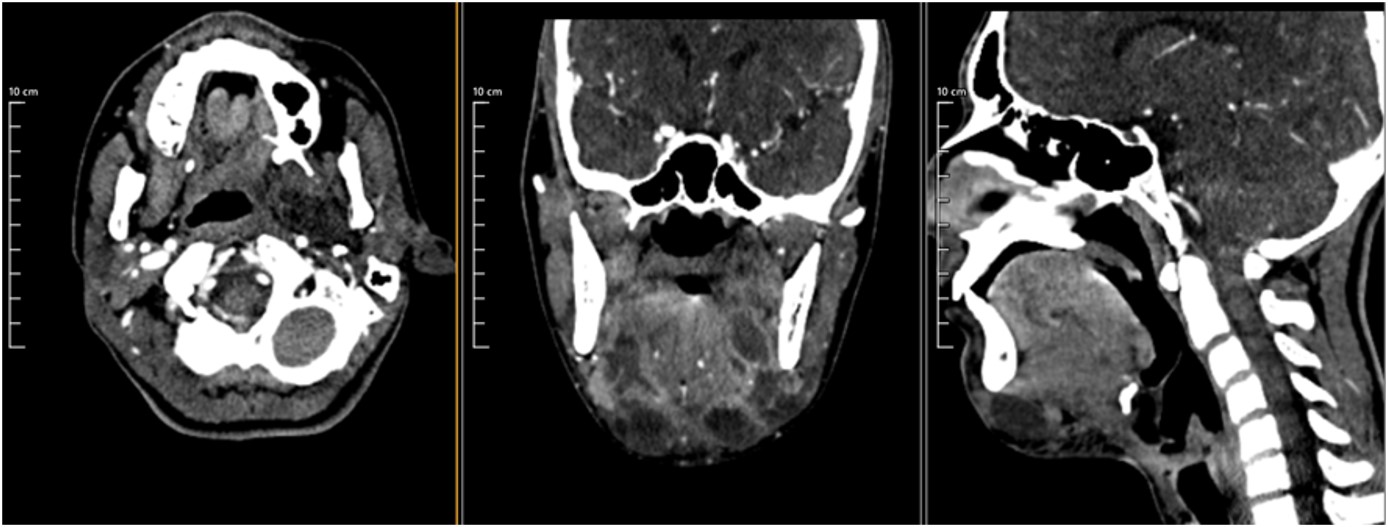
Ludwig’s angina is a serious and potentially fatal disease affecting the neck and floor of the mouth. It is characterized by a rapid progression and is associated with risk factors such as poor oral hygiene and immunosuppression. The disease is caused by a polymicrobial infection, and its treatment is based on adequate airway management, antibiotic therapy and surgical drainage. This report describes a case in which a patient developed Ludwig’s angina from a primary dental infection. Unfortunately, the clinical picture was underestimated, and the disease progressed significantly. It is critical for healthcare professionals to be alert to the signs and symptoms of Ludwig’s angina, especially in patients with risk factors. Timely and appropriate treatment can make a difference in the prognosis of this potentially fatal disease.
Downloads
References
Hansen BW, Ryndin S, Mullen KM. Infections of deep neck spaces. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI. 2020;41(1):74-84.
Esposito S, De Guido C, Pappalardo M, Laudisio S, Meccariello G, Capoferri G, et al. Retropharyngeal, parapharyngeal and peritonsillar abscesses. Children. 2022;9(5):618.
Bridwell R, Gottlieb M, Koyfman A, Long B. Diagnosis and management of Ludwig’s angina: An evidence-based review. Am J Emerg Med. 2021;41:1-5.
Saifeldeen K. Ludwig’s angina. Emerg Med J. 2004;21(2):242-3.
Gunawan F, Ferriastuti W. Ludwig’s angina: An alarming radiology challenge. Radiol Case Rep. 2022;17(9):3103-6.
Romero J, Elkattaway S, Romero A, Latif A, Al-Fiky E, Al-Nasseri A, et al. Ludwig’s angina. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2022;10.
An J, Madeo J, Singhal M. Ludwig angina. En: Stat Pearls [internet]. Treasure Island (FL): Stat Pearls Publishing; 2023 [citado: 2023 nov. 14]. Disponible en: http://www. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482354/
Tami A, Othman S, Sudhakar A, McKinnon BJ. Ludwig’s angina and steroid use: A narrative review. Am J Otolaryngol. 2020;41(3):102411.
Jain A, Singh I, Meher R, Raj A, Rajpurohit P, Prasad P. Deep neck space abscesses in children below 5 years of age and their complications. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;109:40-3.
Oczkowski S, Alshamsi F, Belley-Cote E, Centofanti JE, Hylander Møller M, Nunnaly ME, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines 2021: highlights for the practicing clinician. Pol Arch Intern Med [Internet]. 6 de julio de 2022 [citado: 2023 nov. 14]. Disponible en: https://www.mp.pl/paim/issue/article/16290
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista Colombiana de Radiología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.