Comparative study of Deep Learning models for segmenting abdominal adipose tissue in CT scans
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.280Keywords:
Abdominal fat, Intra-abdominal fat, Tomography, X-Ray computedAbstract
Purpose: Body composition analysis is a test that measures the proportion of various tissues of a person’s body. It serves as an indicator for certain medical conditions such as metabolic syndrome, cancer, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease. Traditionally, these analyses are done using
anthropometric methods or clinical tools that provide an approximated result. Using the family of U-NET Deep Learning architectures, we perform a fully automatic segmentation of visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues. We study these segmentation results and compare them against semiautomatic and manual generated ground truths. Materials and methods: We employ several variations of the U-Net Deep Learning architecture: U-Net, R2U-Net, Attention U-Net, and
Attention R2U-Net. These methods were trained on a dataset, which consists of 554 images from the
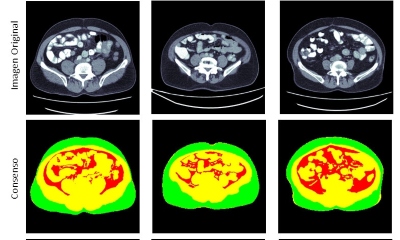
Hospital Universitario San Ignacio and IDIME Institute in Bogota, Colombia, collected from 2015 to 2017. This dataset contains annotations for three different tissues: visceral fat, subcutaneous fat and other tissue generated through semiautomatic segmentation tools. Results: Sørensen-Dice index is used as the evaluation metric against the ground truth which consists of manual segmentations performed by experts. We obtained that the U-Net architecture was the most accurate in terms of overall body composition segmentation, with a mean Dice score of 93.0%, followed closely by the Attention U-Net architecture. Conclusions: We found that the U-Net and Attention U-Net architectures are more suited for body composition analysis. The segmentation results produced by these methods could be used to obtain precise metrics and help physicians understand the patient’s physical condition.
Downloads
References
Afshin A, Vos T, Murray C, Fernandes J, Silverberg J, Bjertness E, et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. New Eng J Med. 2017;377: 13-27
González MC, Pastore C, Orlandi S, Heymsfield S. Obesity paradox in cancer: New insights provided by body composition. Am J Clin Nut. 2014;99
Seabolt LA, Welch EB, Silver HJ. Imaging methods for analyzing body composi¬tion in human obesity and cardiometabolic disease. Ann New York Acad Sci. 2015;1353:41-59
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation [Presentación]. En: Computación de imágenes médicas e intervención asistida por computadora (MICCAI). 2015. Disponible en: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Lee S, Liu J, Yao J, Kanarek A, Summers R, Pickhardt P. Fully automated segmentation and quantification of visceral and subcutaneous fat at abdominal CT: Application to a longitudinal adult screening cohort. Br J Radiol. 2018;91:20170968
Hui SCN, Zhang T, Shi L, Wang D, Ip CB, Chu WCW. Automated segmentation of abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue and visceral adipose tissue in obese adolescent in MRI. Magn Resonan Imag. 2018;45:97-104
Nemoto M, Yeernuer T, Masutani Y, Nomura Y, Hanaoka S, Miki S, et al. Develop¬ment of automatic visceral fat volume calculation software for CT volume data. J Obesity. 2014;2014:495084
Wang Z, Hounye A, Zhang J, Hou M, Qi M. Deep learning for abdominal adipose tissue segmentation with few labelled samples. International J Comp Assis Radiol Surg. 2021;17
Micomyiza C, Zou B, Li Y. An effective automatic segmentation of abdominal adipose tissue using a convolution neural network. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 2022;16:102589
Li H, Luo H, Liu Y. Paraspinal muscle segmentation based on deep neural network. Sensors. 2019;19:2650
Estrada S, Lu R, Conjeti S, Orozco-Ruiz X, Panos-Willuhn J, Breteler MMB, et al. FatSegNet: A fully automated deep learning pipeline for adipose tissue segmentation on abdominal dixon MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2020;83:1471-83
Alom MZ, Hasan M, Yakopcic C, Taha TM, Asari VK. Recurrent residual convolu¬tional neural network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for medical image segmentation [internet]. 2018 [citado: 2023 feb. 15]. Disponible en: https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.06955
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, et al. Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas [internet]. 2018 [citado: 2023 feb. 15]. Disponible en: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.03999
Zhang L, Zuo Q, Chen S, Wang Z. R2AU-Net: Attention recurrent residual convo¬lutional neural network for multimodal medical image segmentation. Sec Commun Net. 2021;2021:6625688
Weston AD, Korfiatis P, Kline TL, Philbrick KA, Kostandy P, Sakinis T, et al. Auto¬mated abdominal segmentation of CT scans for body composition analysis using deep learning. Radiology. 2019;290:669-79
Dabiri S, Popuri K, Cespedes E, Caan B, Baracos V, Beg MF. Deep learning method for localization and segmentation of abdominal CT. Comput Med Imag Graph. 2020;85:101776
Hemke R, Buckless C, Tsao A, Wang B, Torriani M. Deep learning for automated segmentation of pelvic muscles, fat, and bone from CT studies for body composition assessment. Skel Radiol. 2019;49
Koitka S, Kroll L, Malamutmann E, Oezcelik A, Nensa F. Fully automated body composition analysis in routine CT imaging using 3D semantic segmentation convo¬lutional neural networks. Eur Radiol. 2020;31.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista Colombiana de Radiología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.